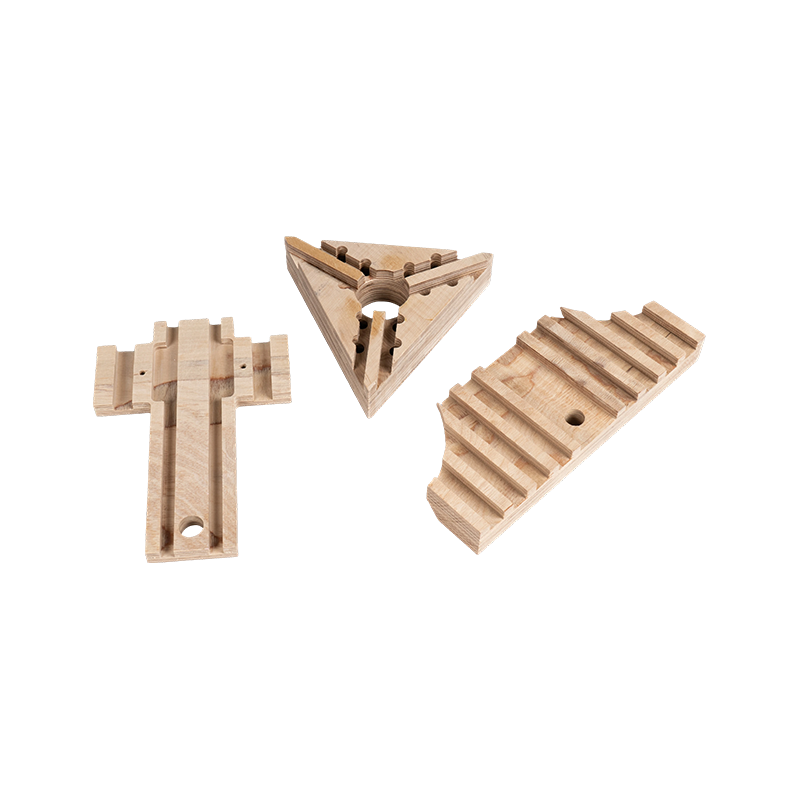
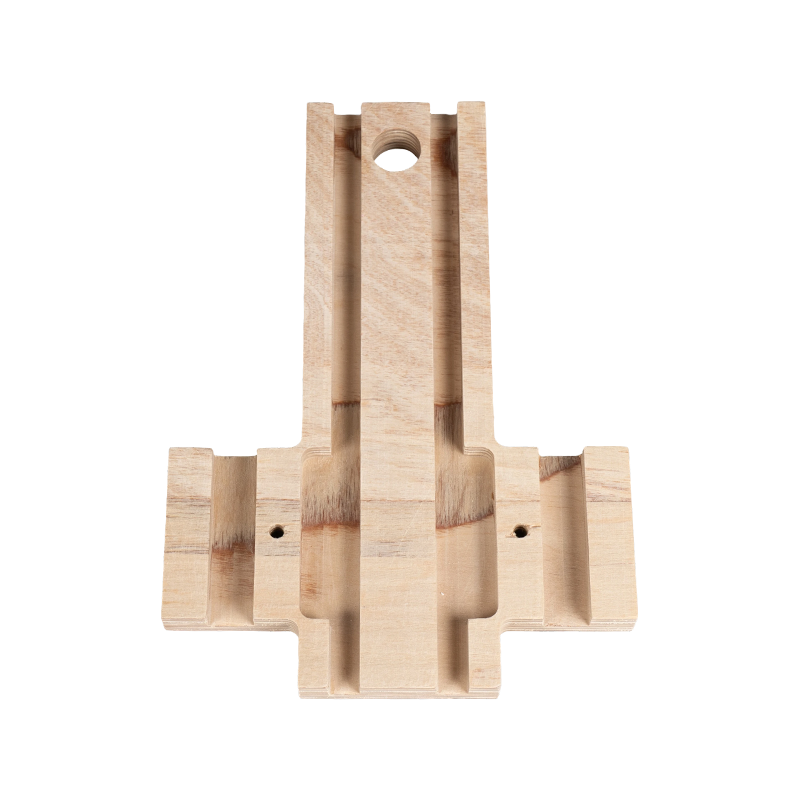
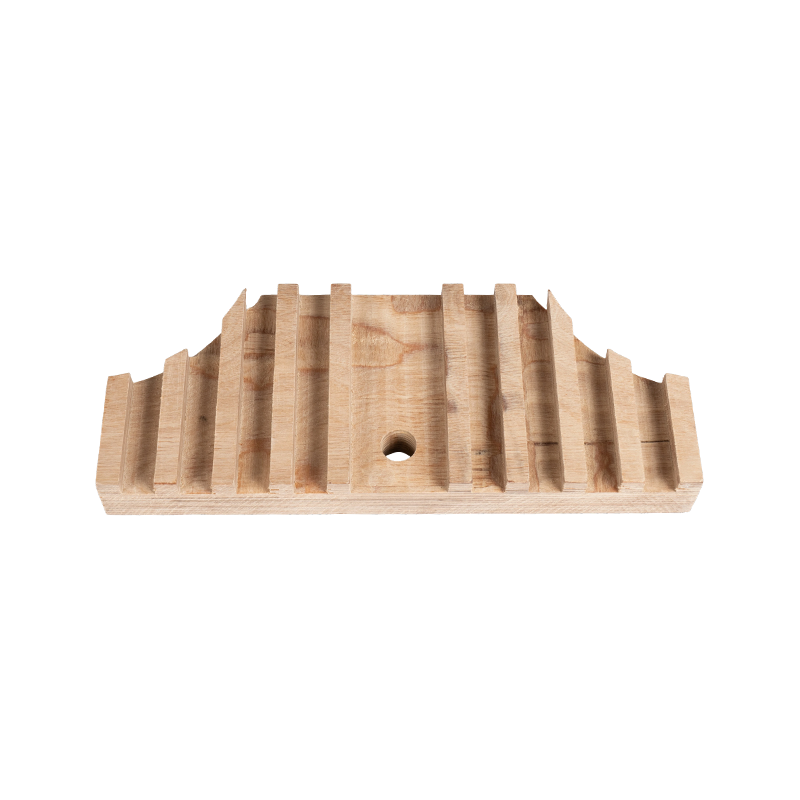
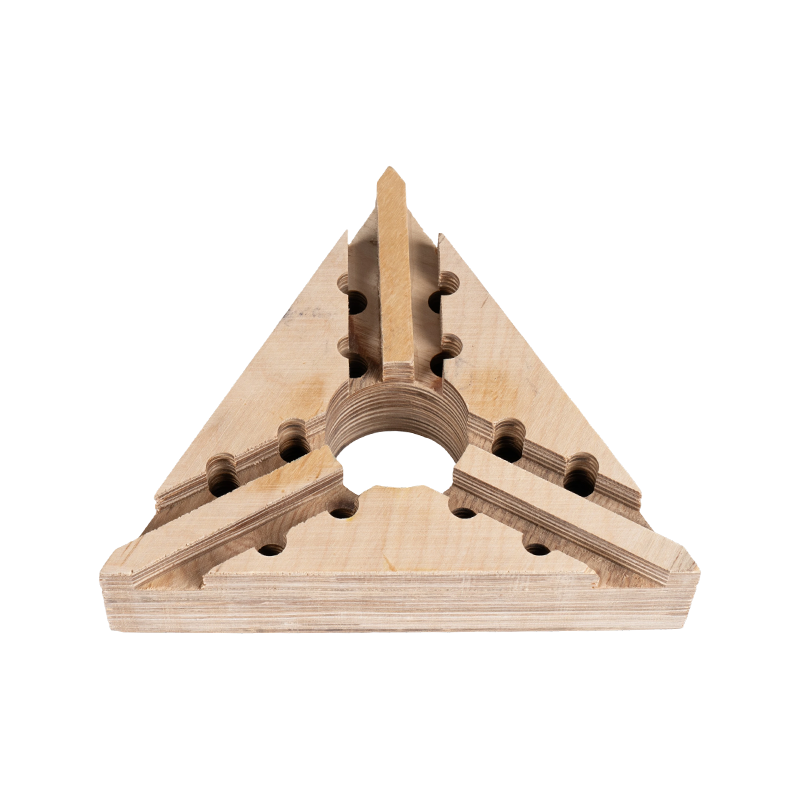
Features:
Functional Integration: Combining the natural properties of wood with the performance of synthetic resins, it achieves integration of structural support and multiple insulation functions (such as electrical and thermal insulation).
Performance Designability: By changing the type, number of layers, orientation, and type of resin used in the wood veneer, it can be engineered to meet specific insulation and strength requirements.
Characteristics:
Electrical Insulation: Possesses good electrical insulation properties.
Environmental Resistance: Some types of products exhibit corrosion resistance and low moisture absorption after treatment, or self-locking properties after immersion in transformer oil.
Flame Retardancy: Its flame retardant properties are enhanced by impregnation with flame retardants or composite bentonite.
Processability: The material weighs approximately one-sixth that of steel and can be machined by drilling, cutting, and other machining processes.
Common Applications:
Power Transformers: Laminated wood is a key material in components such as pressure plates, spacers, and clamps in oil-immersed and dry-type transformers.
Electrical Switchgear: Used as insulating partitions to isolate live parts from grounded parts, preventing short circuits and ensuring the safety of high-voltage systems.
Industrial and Control Systems: Due to its combined thermal and electrical insulation properties, it is used in industrial environments with high levels of heat and electrical exposure, such as control stations and server rooms.
Furniture: Used for durable and stable designs, especially suitable for curved furniture, shelves, and surfaces.


 English
English