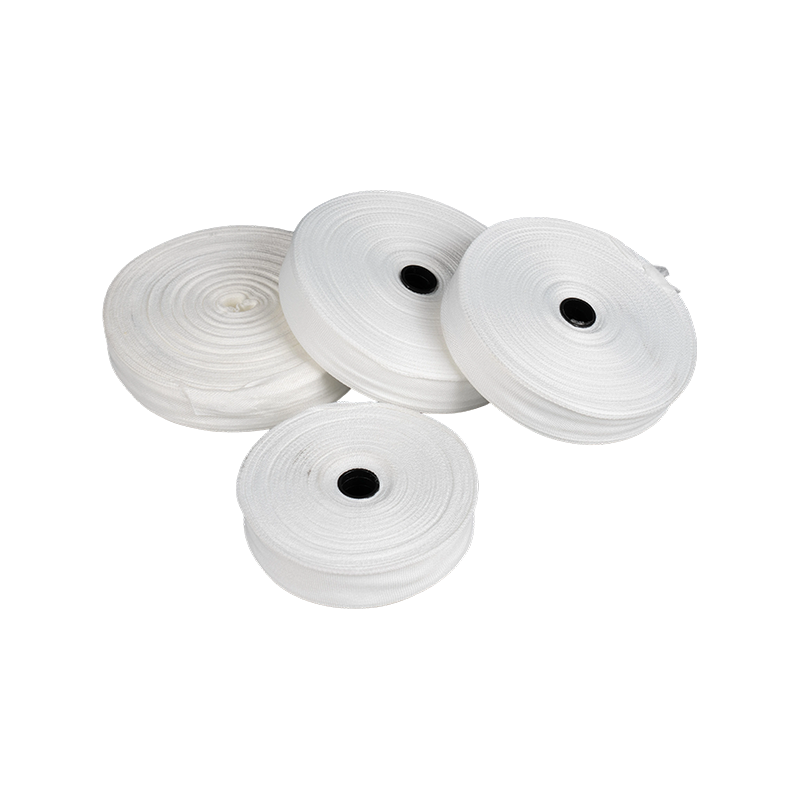
II. Product Performance
1. Stable Heat Resistance: Meeting B/F/H temperature resistance standards, it can operate continuously for extended periods at 130℃, 155℃, and 180℃-200℃ respectively, adapting to the temperature rise requirements of motors and transformers during operation. It exhibits strong resistance to high-temperature aging.
2. Excellent Mechanical Strength: High tensile strength; the tensile strength of a 0.3mm thick product can reach over 1500N/cm, with a maximum binding force of up to 1500N/cm. After curing, it possesses sufficient rigidity and impact resistance, along with high modulus and low elongation, enabling it to stably withstand vibrations and electrodynamic forces during equipment operation.
3. Excellent Insulation and Electrical Performance: Outstanding electrical insulation; the breakdown voltage of the parallel winding layer is ≥12kV/mm, with some models reaching over 20kV. It meets standards for arc resistance and tracking resistance, with no hysteresis or eddy current loss, avoiding the risk of insulation failure.
4. Convenient Construction and Storage: High curing efficiency, curing completes in just 3-5 hours at 155℃, saving labor time; easy to process, can be tied manually or automatically, with better results when hot-stitched; temperature control is required for storage, can be stored for 2-6 months below 30℃, and up to 12 months at ≤5℃, refrigerated storage is required in high-temperature environments.
III. Product Applications
The core of the non-woven tape is used in the manufacturing and maintenance of motors, transformers, and instrument transformers. Its core functions are binding, fastening, and insulation protection. Specific scenarios are as follows:
1. Motor Field: Suitable for DC motors, traction motors, generators, etc., mainly used for winding and binding rotor and stator coils. It can also strengthen the internal winding structure of the motor, improve the winding's vibration and impact resistance, and ensure the structural stability of the motor during high-speed operation.
2. Transformer Applications: Primarily used for securing the core and high/low voltage coils, filling coil gaps, dispersing electric field stress, strengthening insulation between the coil and core, and between the coil and casing, reducing partial discharge, and adapting to the insulation binding requirements of various dry-type and oil-immersed transformers.
3. Instrument Transformer Applications: As the core binding material for the internal coils of instrument transformers, it combines insulation protection and structural fixation, adapting to the winding of current transformers and voltage transformers, ensuring the insulation reliability and operational stability of instrument transformers under high-voltage conditions.
4. Extended Applications: Also used for winding and binding of surge arresters, welding machines, high-voltage vessels, and other electrical equipment, adapting to the insulation and fastening requirements of various high-voltage electrical equipment.
| Temperature Resistance Class | Common Thickness (mm) | Width Range (mm) | Tensile Strength (N/cm) | Maximum Binding Force (N/cm) | Breakdown Voltage (kv/mm) | Curing Conditions (Temperature/Time) | Storage Conditions (Temperature/Shelf Life) |
| Class B (130℃) | 0.17, 0.3 | 6–50 | ≥1200 | ≥1000 | ≥12 | 130℃/4–6h | ≤30℃/2 months; ≤5℃/6 months |
| Class F (155℃) | 0.3, 0.33 | 6–80 | ≥1500 | ≥1200 | ≥15 | 155℃/3–5h | ≤30℃/3 months; ≤5℃/9 months |
| Class H (180–200℃) | 0.33, 0.4 | 10–120 | ≥1800 | ≥1500 | ≥20 | 180℃/2–3h | ≤30℃/1 month; ≤5℃/12 months |


 English
English