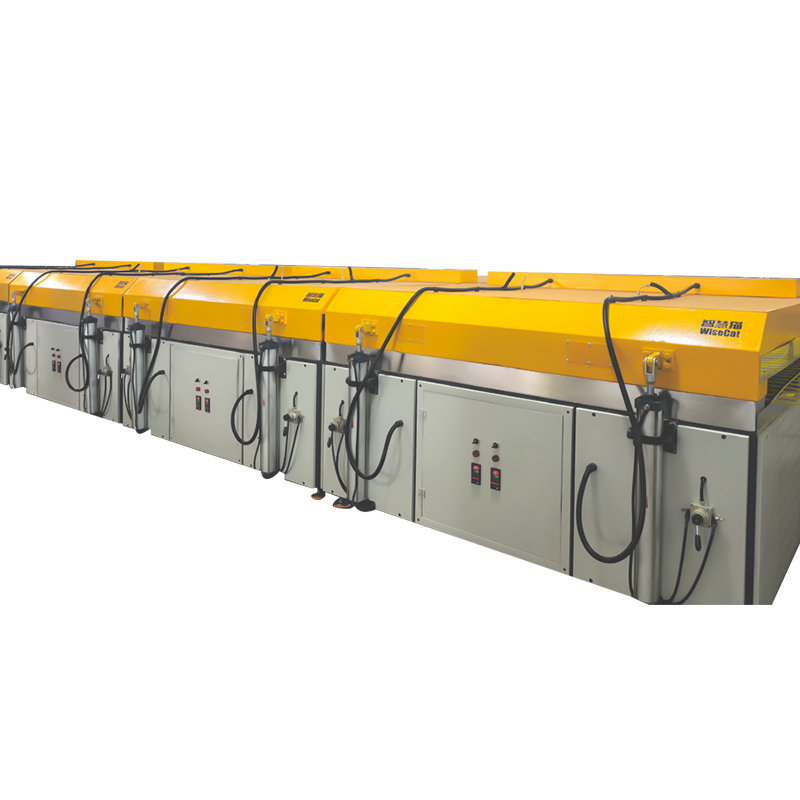
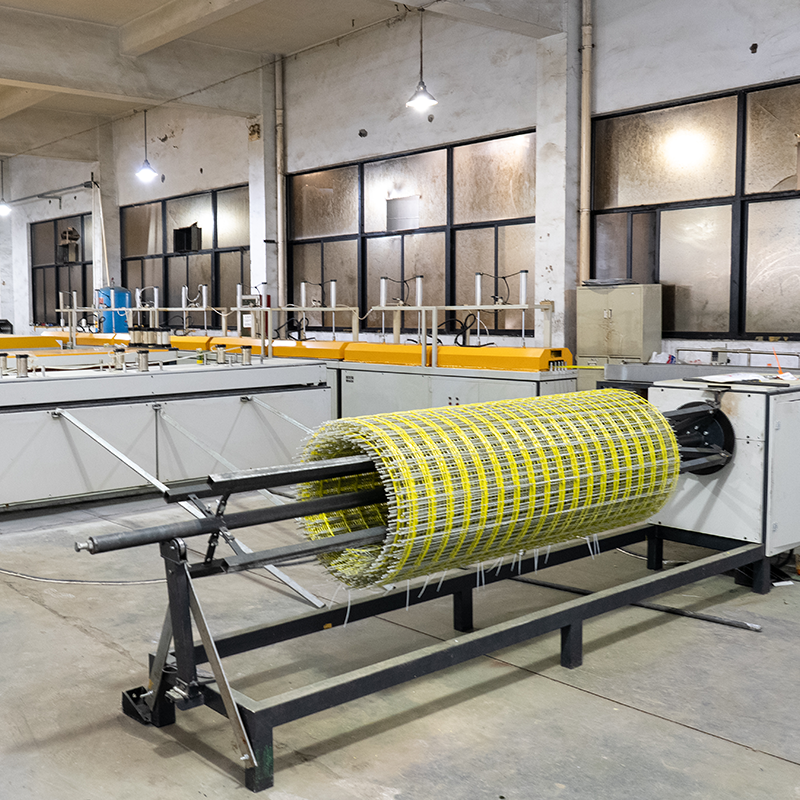
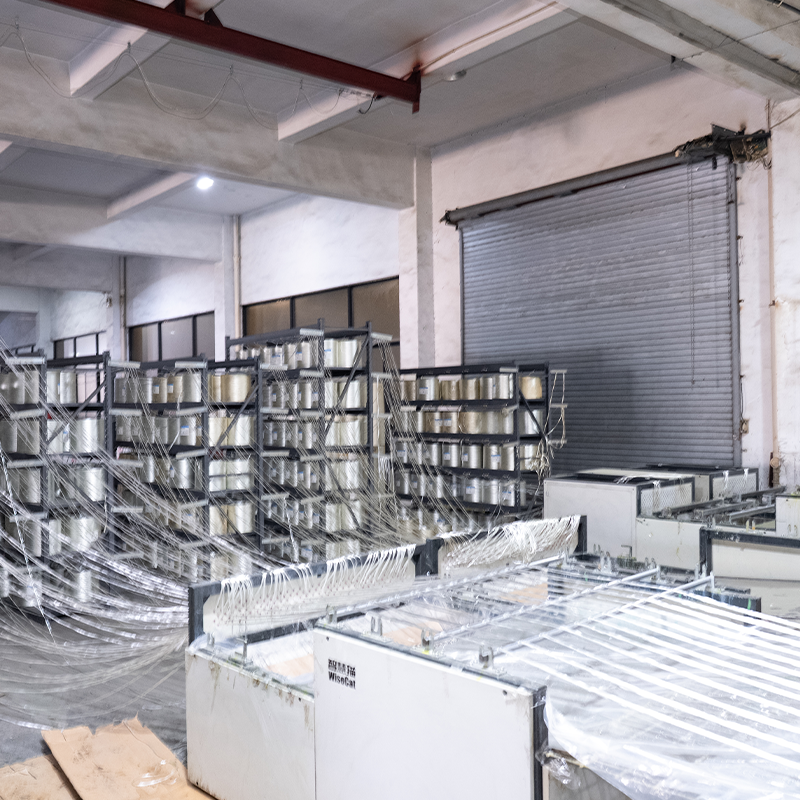
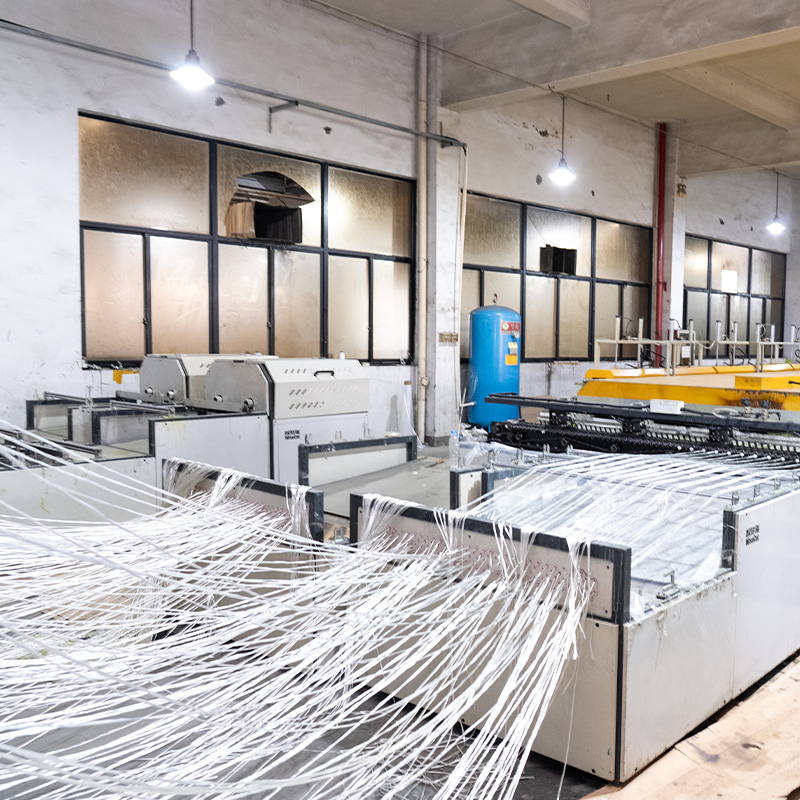
Technical Advantages:
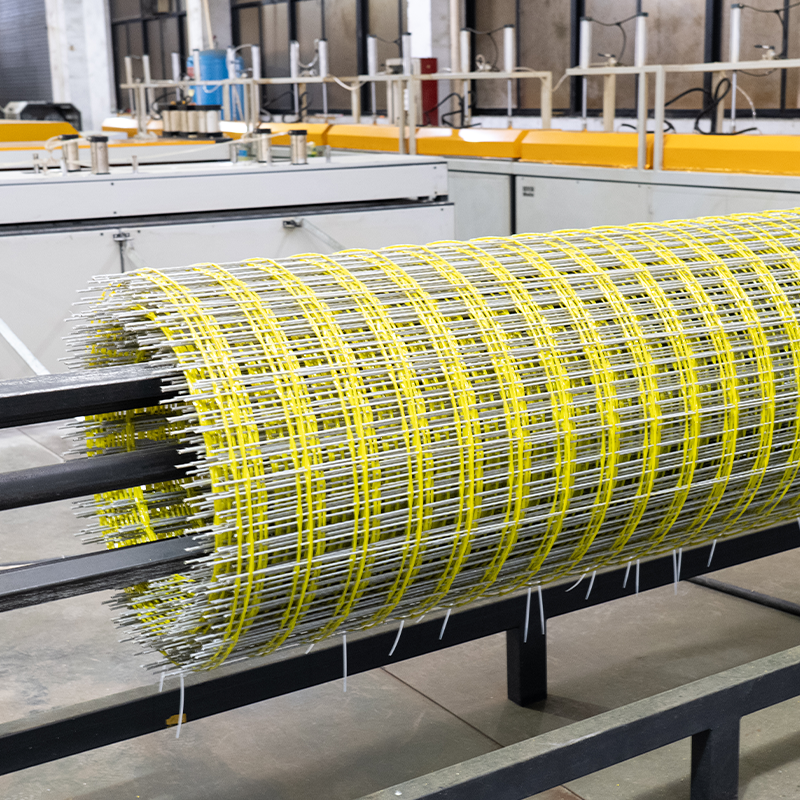
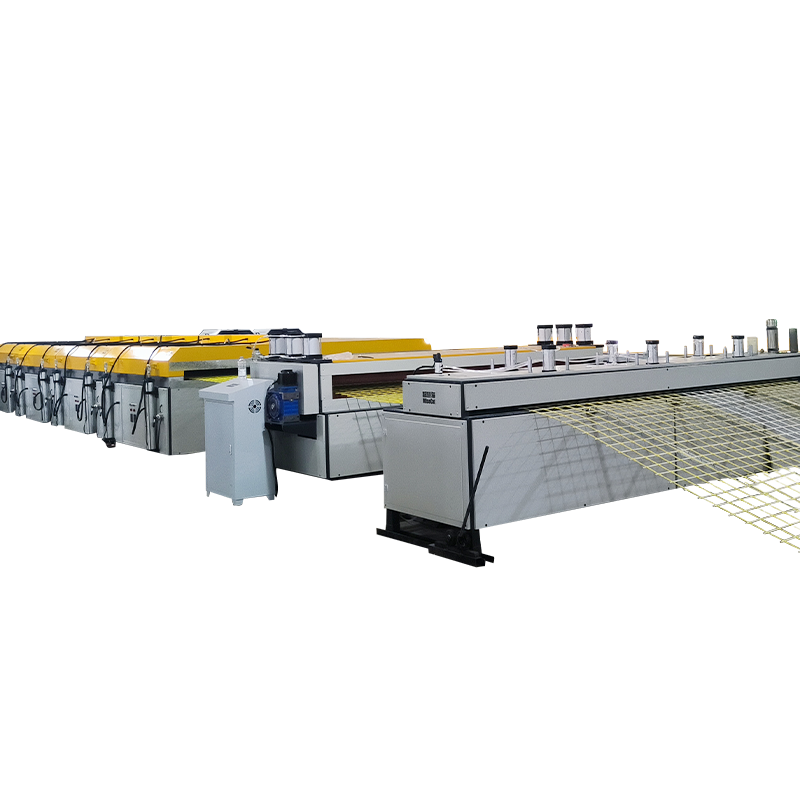
The core of the production line lies in achieving uniform impregnation and precise molding of continuous fibers. For example, its impregnation tank design ensures that glass fiber bundles (such as alkali-free glass fibers) are fully impregnated in matrices such as unsaturated polyester resin and vinyl ester resin; combined with molding dies, the mesh's aperture size, fiber orientation, and cross-sectional shape can be precisely controlled. The curing stage primarily employs energy-efficient and high-performance ultraviolet (UV) curing technology, equipped with even light irradiation and protective devices. This not only improves curing quality but also ensures environmental protection and operational safety. Some production lines have also introduced three-dimensional weaving or spaced continuous fabric technology, enabling the production of three-dimensional mesh structures that significantly improve the overall mechanical properties and fiber volume content of the product.
Key Components:
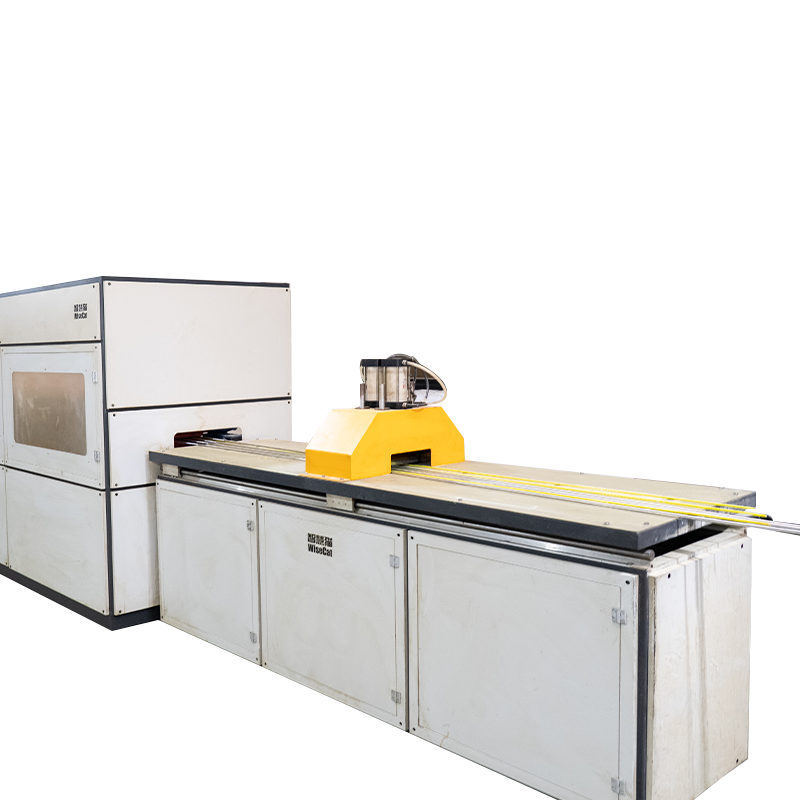
Fiber Yarn Frame and Guide System: Orderly places glass fiber yarn bundles and guides the fibers into subsequent processes, ensuring continuous and uniform fiber transport.
Impregnation Device: One of the core components, allowing the fiber bundles to be fully impregnated with liquid resin, ensuring complete resin coating of the fibers.
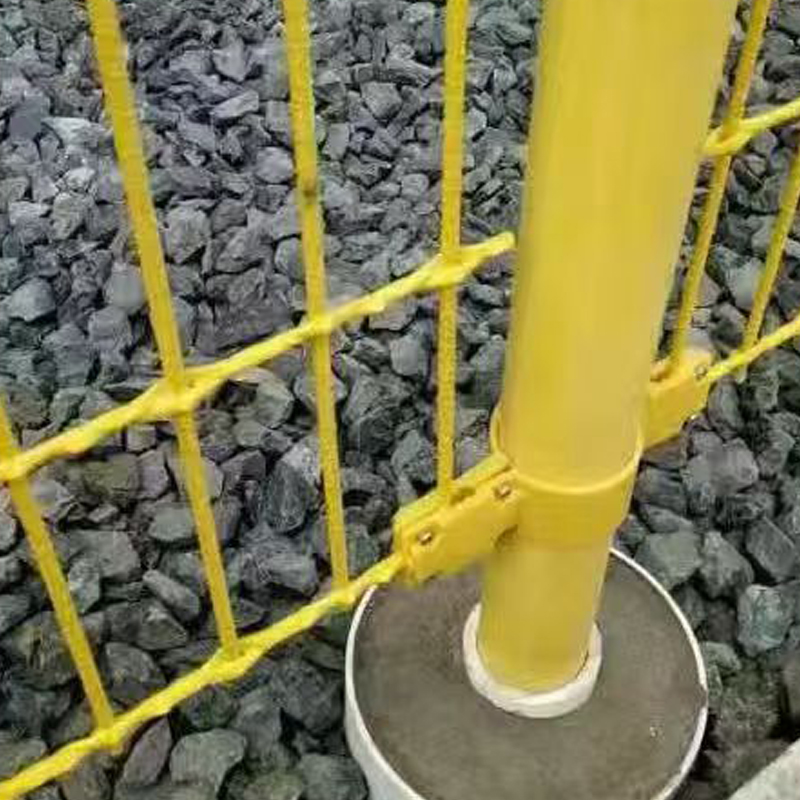
Molding and Winding Device: Gives the impregnated fibers a specific cross-sectional shape and mesh structure, such as determining the reinforcing bar diameter or mesh morphology.
Curing and Molding System: Transforms the resin from a liquid to a solid state through specific methods (such as UV irradiation), completing the final shaping.
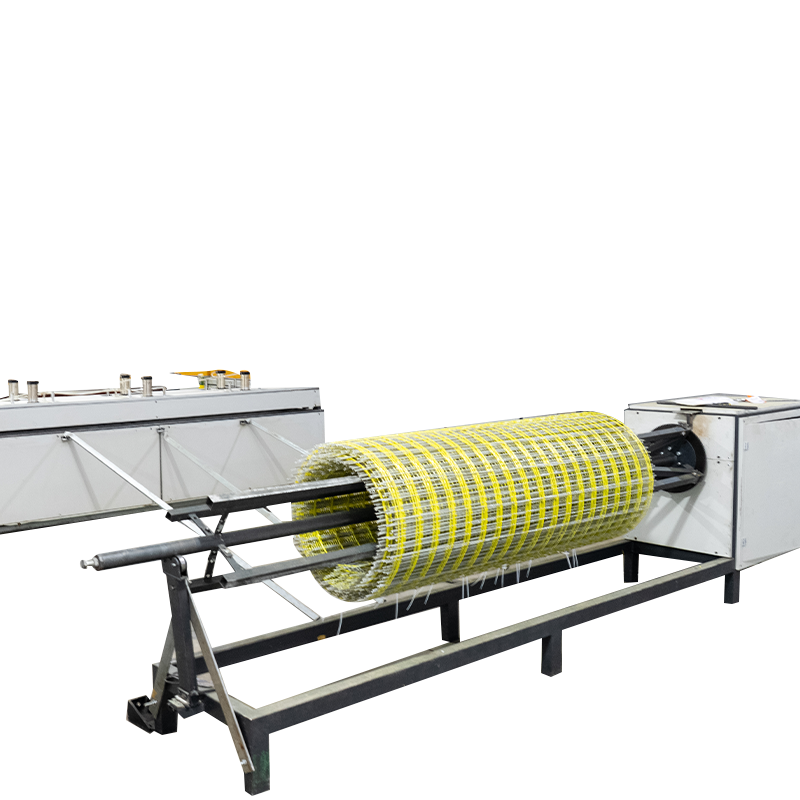
Traction and Cutting Equipment: Provides stable power to continuously extract the product from the production line and precisely cuts it to the required length.
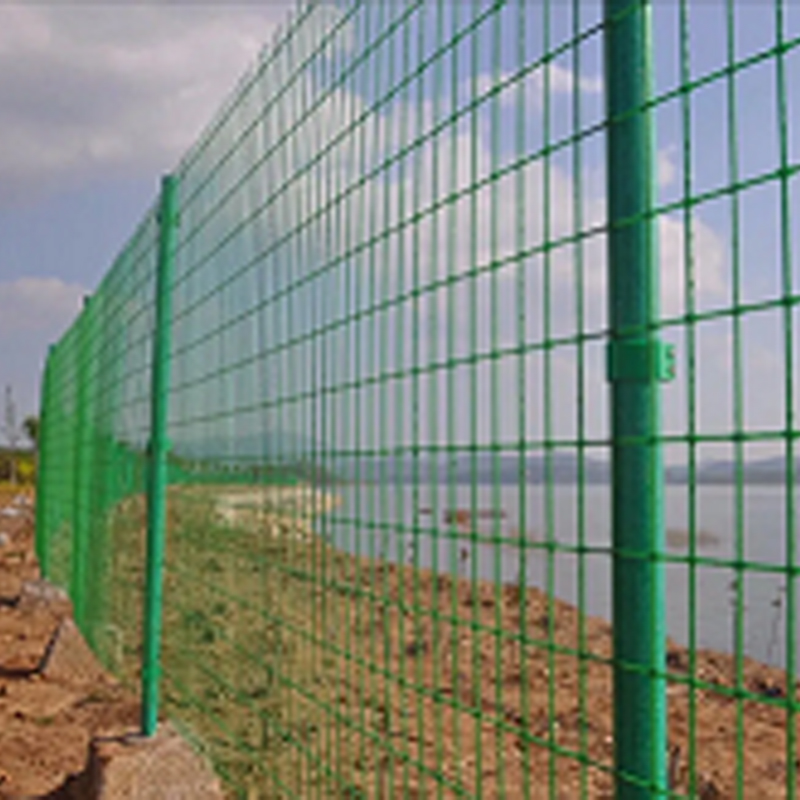
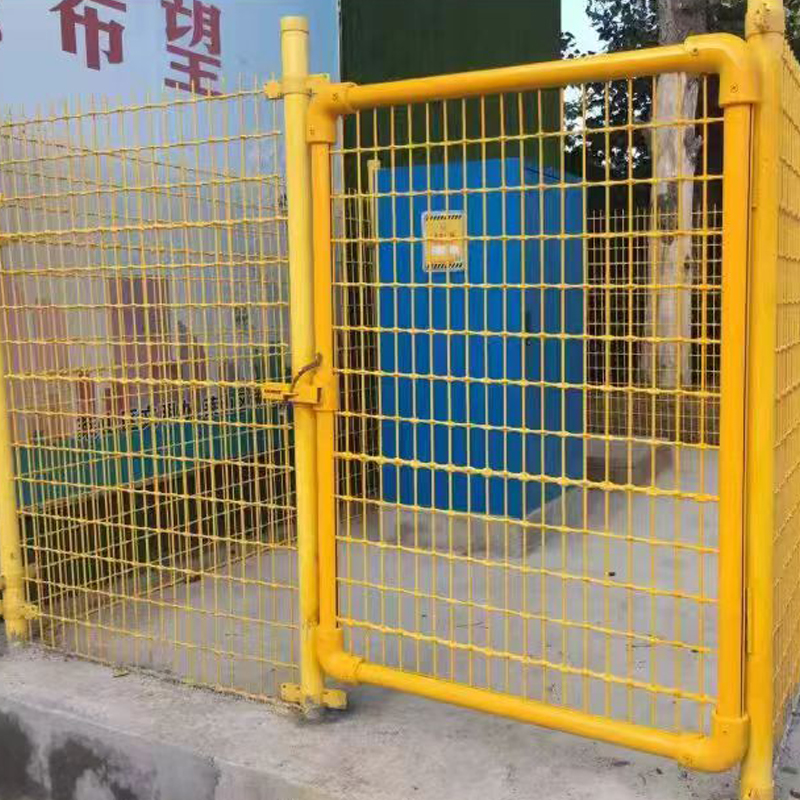
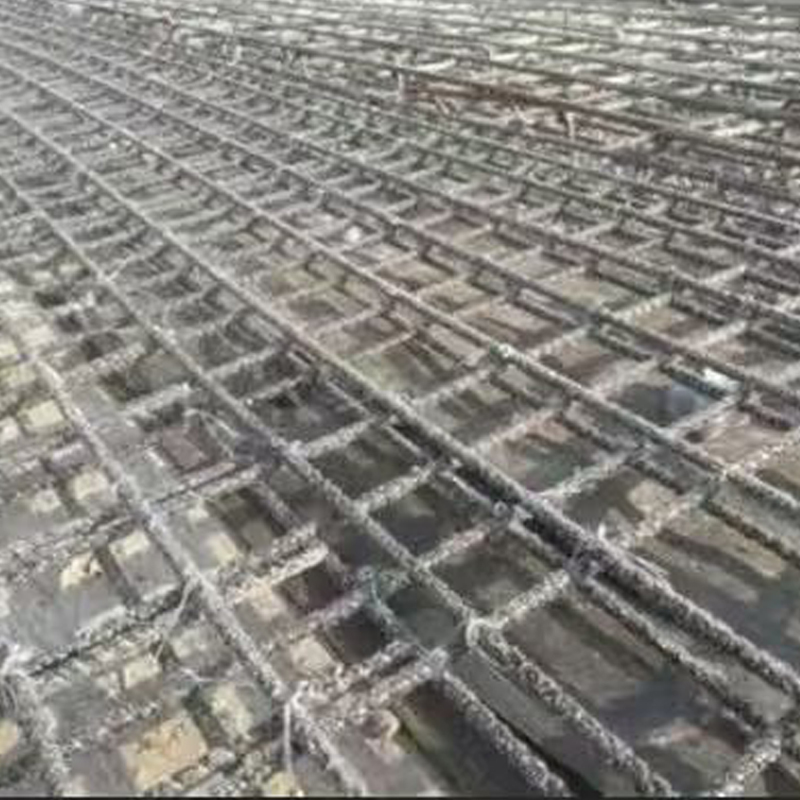
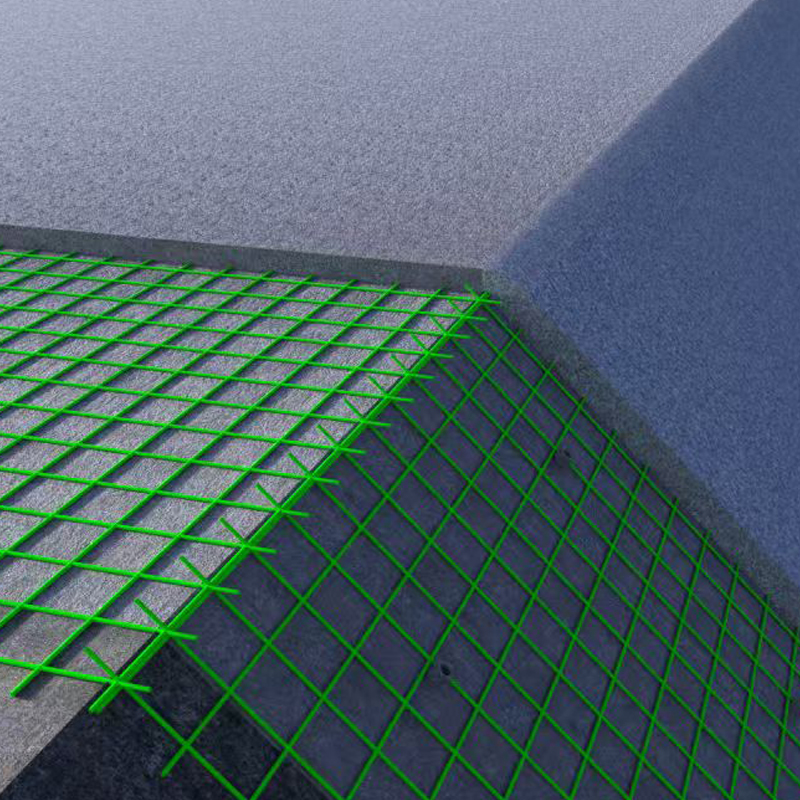
Product Features: GFRP mesh is corrosion-resistant, resisting erosion from acids, alkalis, salts, and other chemical media, resulting in a long service life. It is lightweight and high-strength, with a density approximately 1/4 that of steel, but its strength far exceeds that of ordinary steel, effectively reducing structural weight. It is electrically insulating and non-magnetic, making it suitable for electromagnetically sensitive environments; it also possesses flame-retardant, anti-slip, and fatigue-resistant properties.
GFRP mesh is widely used in:
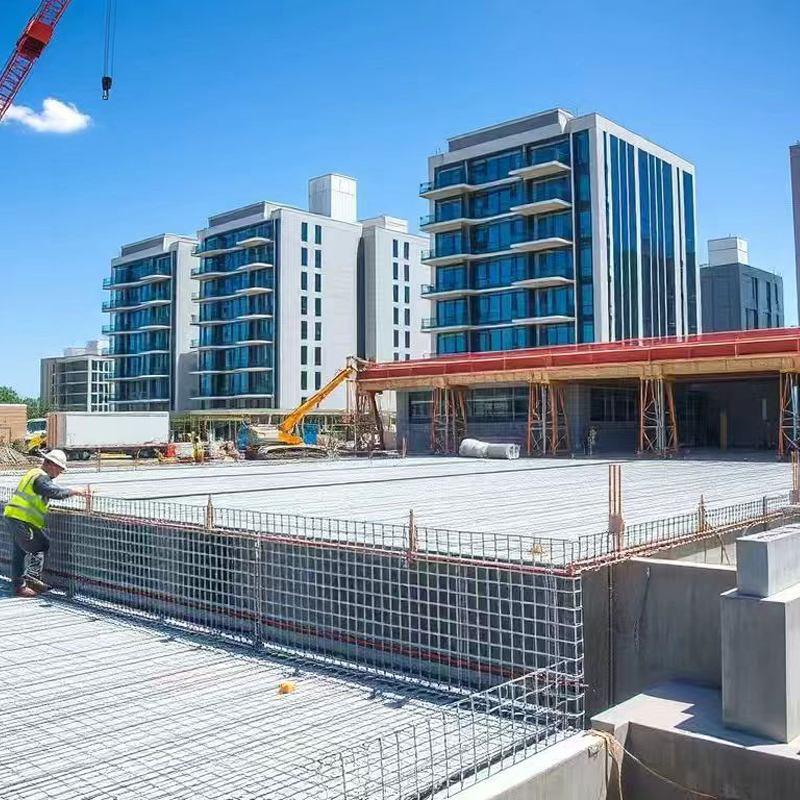
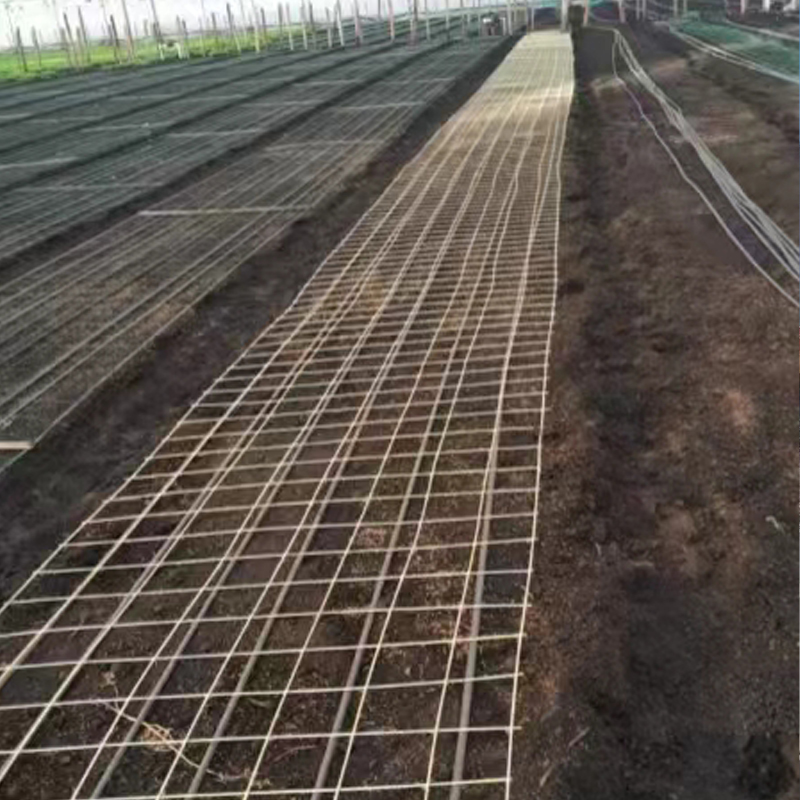
Construction Engineering: Used as reinforcing bars (FRP reinforcement), reinforcement mesh, and formwork in concrete structures, especially in corrosive environments (such as chemical plants and coastal buildings) to replace steel bars and solve corrosion problems.
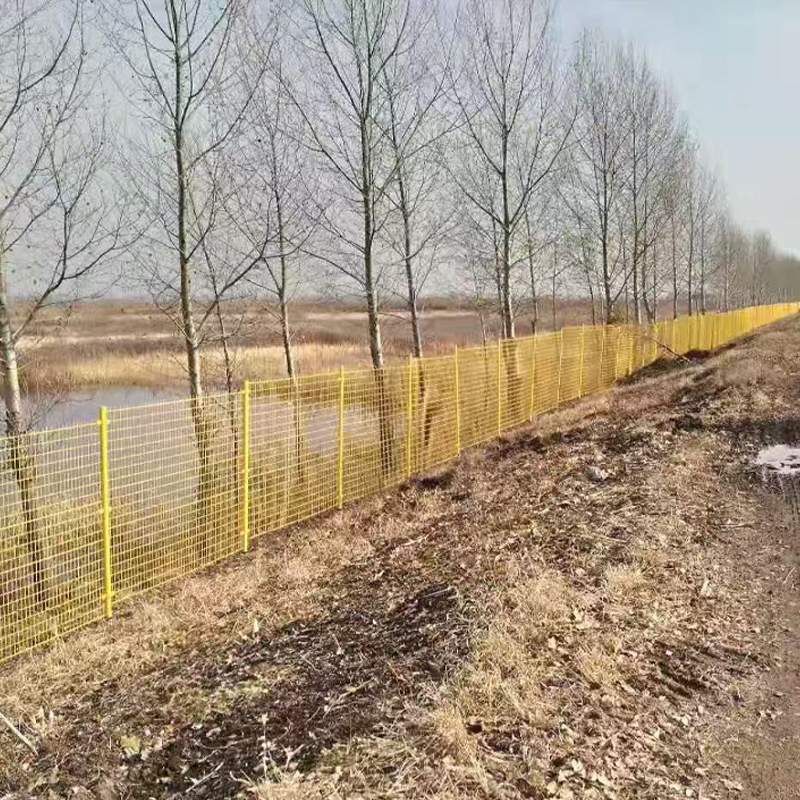
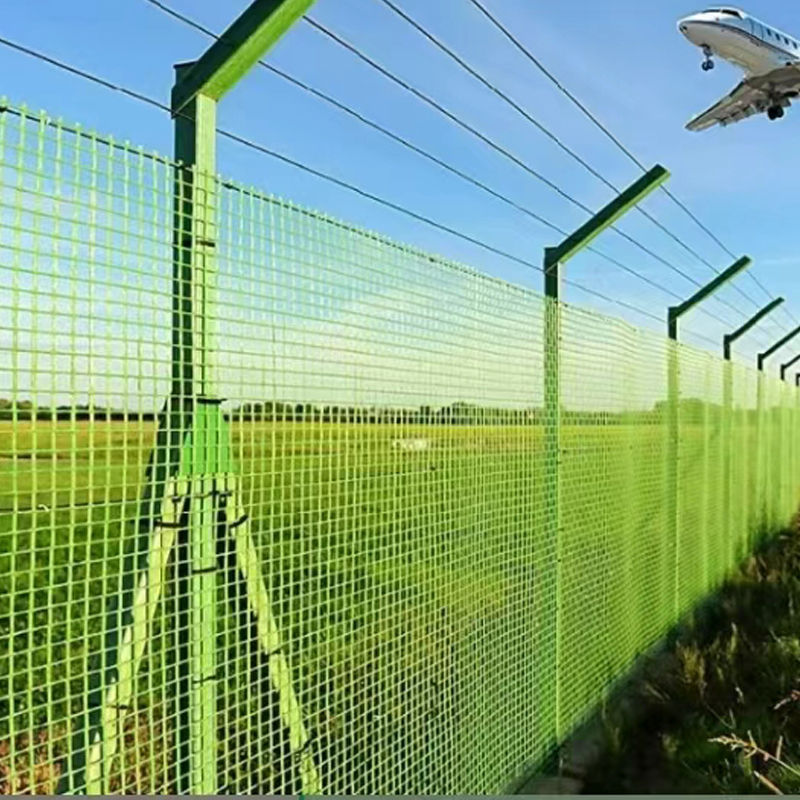
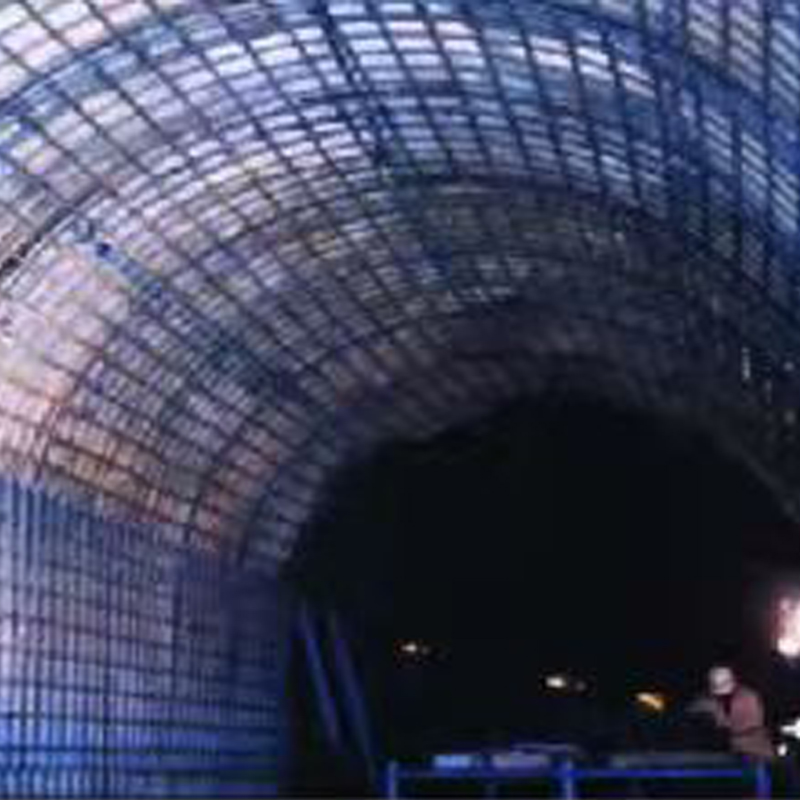
Infrastructure: Used for maintenance walkways, trench covers, and trash racks in water treatment plants; as the base material for road and bridge railings; and for tunnel linings.
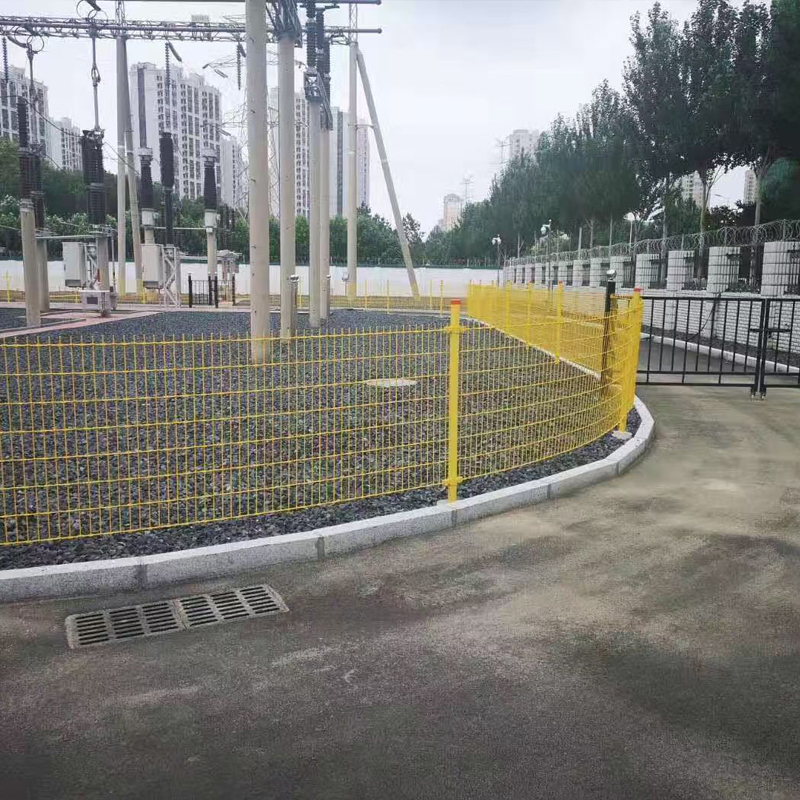
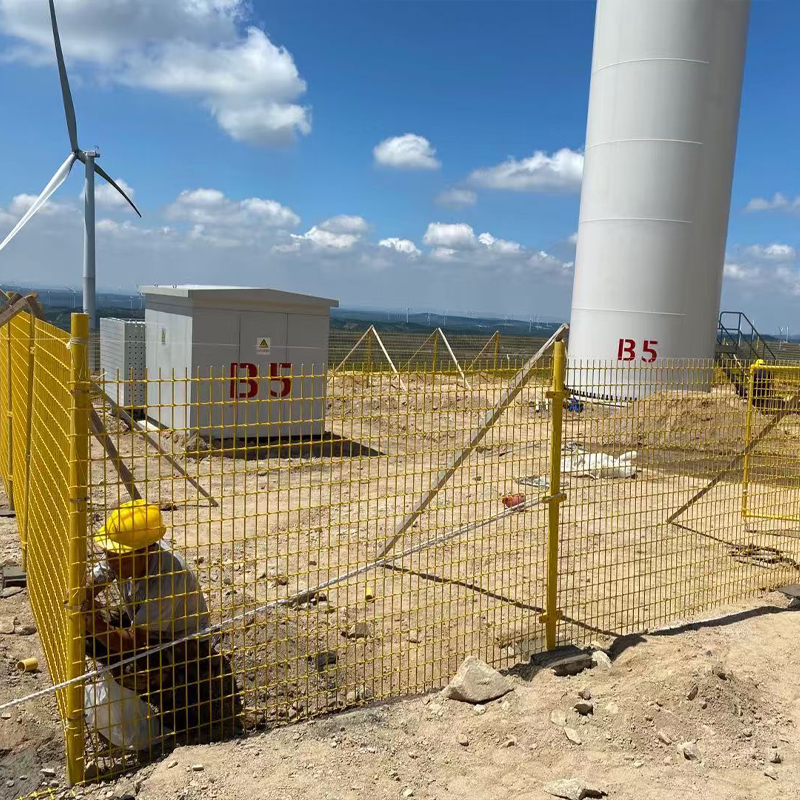
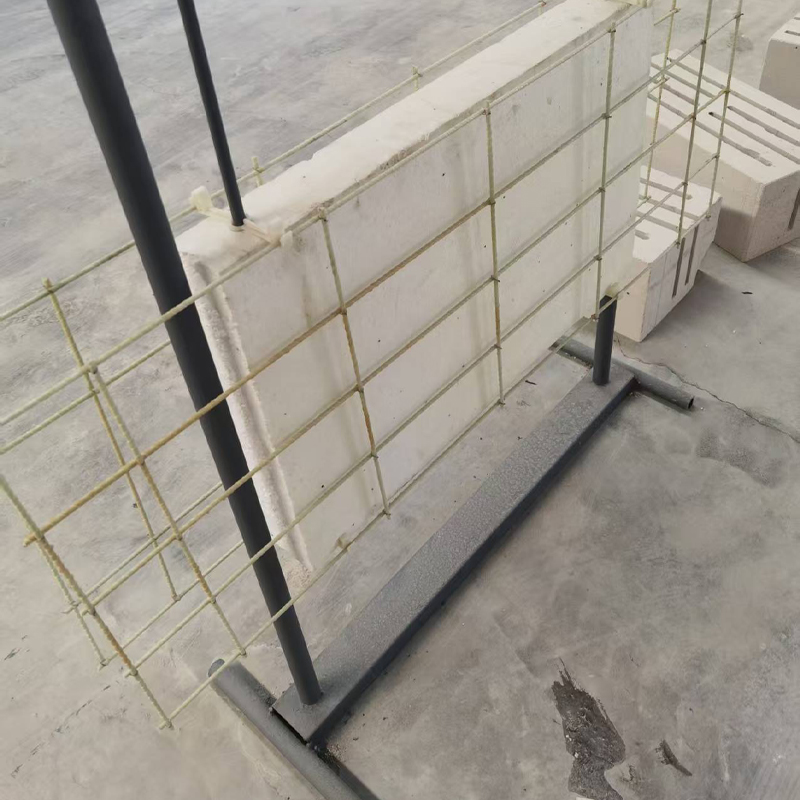
Industrial Platforms: Used in corrosive or insulation-requiring environments such as oil platforms, power plants, and electronics workshops for fabricating operating platforms, stair treads, and fencing systems.
Other Fields: Also used in ship decks, lightweight automotive components, and sports equipment.


 English
English